what is the sugar in atp called Nucléotide, c'est quoi?
Hello everyone! I hope you are all doing well. Today I wanted to talk a little bit about glucose and ATP, two very important biomolecules in our body. The first image we have is a great visual representation of the chemical structure of glucose and ATP, and how they are related. Glucose is a type of sugar and is one of the primary sources of energy in our body. When glucose is broken down in cellular respiration, it produces ATP, which is the energy currency of our cells.
Glucose: The Fuel That Powers Our Cells!
Glucose is a simple sugar that is found in many foods, such as fruits and vegetables, and is produced by plants through the process of photosynthesis. Once we consume glucose, our body breaks it down into smaller molecules in a process called glycolysis. These smaller molecules are then converted into ATP, which our cells use to power essential cellular processes, such as muscle contraction and the regulation of body temperature.
 Glucose is not only an important source of energy, but it also plays a critical role in other physiological functions such as regulating blood sugar levels. Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, helps to regulate glucose levels in the blood. When our blood sugar levels are too high, insulin helps to store excess glucose in the liver and muscle tissue. When our blood sugar levels are too low, glucagon, another hormone produced by the pancreas, helps to release stored glucose back into the bloodstream.
Glucose is not only an important source of energy, but it also plays a critical role in other physiological functions such as regulating blood sugar levels. Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, helps to regulate glucose levels in the blood. When our blood sugar levels are too high, insulin helps to store excess glucose in the liver and muscle tissue. When our blood sugar levels are too low, glucagon, another hormone produced by the pancreas, helps to release stored glucose back into the bloodstream.
Photosynthesis: The Ultimate Source of Energy
The second image we have is a great visual representation of the process of photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy in the form of glucose. During photosynthesis, plants use carbon dioxide and water to produce glucose and oxygen. This process not only provides energy for the plant itself but also provides energy for all the other organisms that consume plants or other organisms that have consumed plants.
.PNG)
In conclusion, glucose and ATP are two of the most important biomolecules in our body. Glucose provides the fuel our cells need to function properly, while ATP is the energy currency that powers all of our cellular processes. Additionally, photosynthesis is the ultimate source of energy for all life on Earth and plays a critical role in maintaining a habitable planet.
If you are searching about Photosynthesis - Presentation Biology you’ve came to the right page. We have 5 Pics about Photosynthesis - Presentation Biology like Photosynthesis - Presentation Biology, Glucose; ATP / Koolhydraten / biomoleculen | BioByMBO and also Photosynthesis - Presentation Biology. Here you go:
Photosynthesis - Presentation Biology
.PNG)
Glycolysis - SNC1D - BIOLOGY LESSON PLAN BLOG
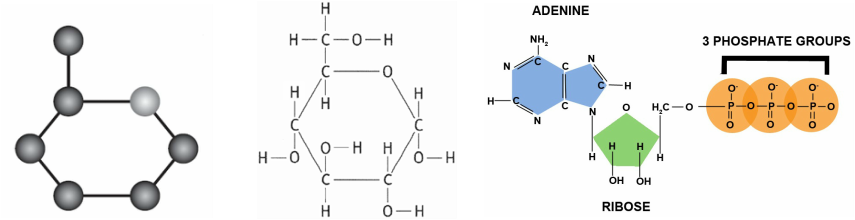 sbi4uraft2014.weebly.comglycolysis lesson glucose atp molecules weebly
sbi4uraft2014.weebly.comglycolysis lesson glucose atp molecules weebly
11.7 – Gene Regulation: Operon Theory – Microbiology 201
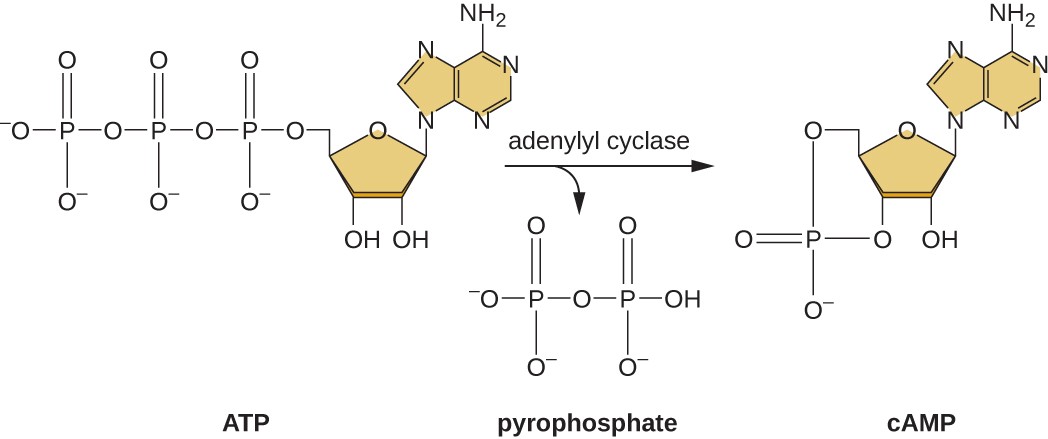 psu.pb.unizin.orgatp operon depletion decrease
psu.pb.unizin.orgatp operon depletion decrease
Nucléotide, C’est Quoi? | Cabinet Médical Empuriabrava
 medicoempuriabrava.comGlucose; ATP / Koolhydraten / Biomoleculen | BioByMBO
medicoempuriabrava.comGlucose; ATP / Koolhydraten / Biomoleculen | BioByMBO
 biomoleculenmbo.jouwweb.nlatp glucose procesos metabolicos
biomoleculenmbo.jouwweb.nlatp glucose procesos metabolicos
11.7 – gene regulation: operon theory – microbiology 201. Atp glucose procesos metabolicos. Nucléotide, c’est quoi?