can type 2 diabetics get diabetic ketoacidosis Dka ketoacidosis diabetic pathophysiology powerpoint
Diabetes is a chronic disease that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a condition that affects the way the body processes glucose, the primary source of energy for the body’s cells. There are two main types of diabetes - Type 1 and Type 2. Type 1 diabetes occurs when the body’s immune system attacks the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin, a hormone that helps regulate glucose levels in the blood. Type 2 diabetes, on the other hand, is a condition where the body becomes resistant to insulin, and the pancreas is unable to produce enough insulin to compensate. One of the complications that can arise from diabetes is diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). It is a potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when the body starts to break down fat for energy instead of glucose. This process produces ketones that can build up in the blood and cause the blood to become acidic. If left untreated, DKA can lead to coma and even death. While DKA is more commonly associated with Type 1 diabetes, it can also occur in Type 2 diabetes in certain situations. In this post, we’ll explore the difference between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes regarding DKA and why the latter is less likely to develop this complication. Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in children and young adults and requires lifelong insulin therapy. This is because the body is unable to produce insulin. As a result, glucose cannot enter the body’s cells, and the body is forced to break down fat for energy. This process leads to the production of ketones, which can build up in the blood and cause DKA. However, with proper insulin therapy, Type 1 diabetes can be managed, and the risk of developing DKA can be minimized. Type 2 diabetes, on the other hand, develops when the body becomes resistant to insulin, and the pancreas cannot produce enough insulin to compensate. In Type 2 diabetes, the body is still able to use glucose for energy, but it cannot use it effectively. As a result, glucose can build up in the blood and cause hyperglycemia, which can be managed with medication, lifestyle changes, and, in some cases, insulin therapy. In general, Type 2 diabetes is less likely to lead to DKA than Type 1 diabetes. This is because in Type 2 diabetes, the body is still able to use glucose for energy, and there is less reliance on fat breakdown for energy. Additionally, the body of a person with Type 2 diabetes is usually able to compensate for the lack of insulin by producing more. However, there are some situations where the risk of DKA is higher in Type 2 diabetes, such as during illness or infection, which can cause insulin resistance and lead to a buildup of ketones in the blood. In conclusion, while DKA is more commonly associated with Type 1 diabetes, it can also occur in certain situations in Type 2 diabetes. However, because the body of a person with Type 2 diabetes is still able to use glucose for energy, the risk of DKA is generally lower. It is essential for people with diabetes, whether Type 1 or Type 2, to be aware of the signs and symptoms of DKA and seek medical attention immediately if they suspect they may be developing this complication. With proper management and education, the risk of developing DKA can be minimized, and persons with diabetes can enjoy a better quality of life.
If you are looking for Warning Issued By FDA Regarding Type 2 Diabetes Drugs — Survive The End you’ve came to the right web. We have 5 Pics about Warning Issued By FDA Regarding Type 2 Diabetes Drugs — Survive The End like Warning Issued By FDA Regarding Type 2 Diabetes Drugs — Survive The End, Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) - PowerPoint Slides and also Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) - PowerPoint Slides. Here it is:
Warning Issued By FDA Regarding Type 2 Diabetes Drugs — Survive The End
 survivetheenddays.comketoacidosis diabetes type diabetic mechanism drugs issued regarding fda warning
survivetheenddays.comketoacidosis diabetes type diabetic mechanism drugs issued regarding fda warning
Why Do Type 2 Diabetics Not Get Ketoacidosis | DiabetesTalk.Net
 diabetestalk.nettype diabetics diabetes diabetestalk insulin
diabetestalk.nettype diabetics diabetes diabetestalk insulin
DKA: Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Hohman Rehab Physical Therapy
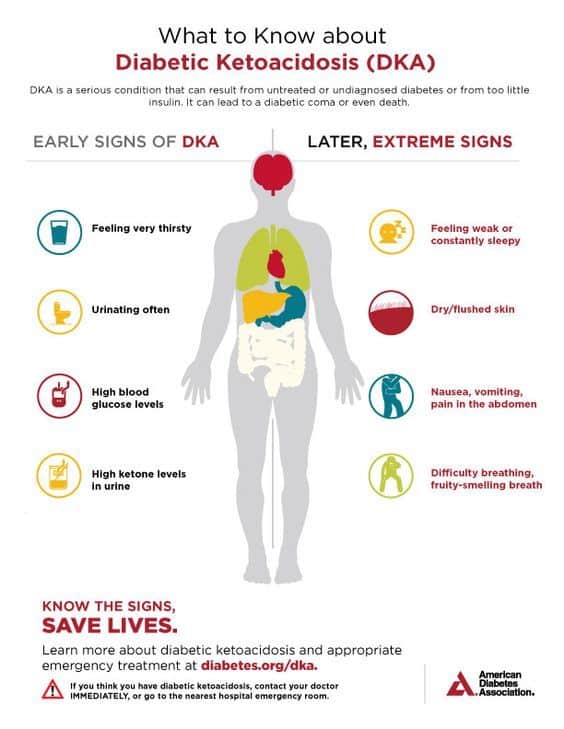 hohmanrehab.comketoacidosis diabetic dka diabetes type nursing symptoms blood sugar signs infographic ketosis diet low facts keto mellitus deadly notes prevent
hohmanrehab.comketoacidosis diabetic dka diabetes type nursing symptoms blood sugar signs infographic ketosis diet low facts keto mellitus deadly notes prevent
Nursing Care Plan For Diabetes Ketoacidosis : 4 Type 1 Diabetes
 revelacionesyespiritualidad.blogspot.comdiabetes ketoacidosis causes complications dka diabetic symptome mellitus nursing ketosis fruity ketones anzeichen mantracare ursachen abdominal urine coma being
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) - PowerPoint Slides
_1541410883_40244-7.jpg) www.myprivatetutor.mydka ketoacidosis diabetic pathophysiology powerpoint
www.myprivatetutor.mydka ketoacidosis diabetic pathophysiology powerpoint
Why do type 2 diabetics not get ketoacidosis. Nursing care plan for diabetes ketoacidosis : 4 type 1 diabetes. Type diabetics diabetes diabetestalk insulin